 NA-MIC Project Weeks
NA-MIC Project Weeks
Back to Projects List
Slicer-Liver: liver resection planning in 3D Slicer
Key Investigators
- Rafael Palomar (Oslo Unviersity Hospital and NTNU)
- Gabriella d’Albenzio (Oslo University Hospital)
- Ole Vegard Solberg (SINTEF)
- Geir Arne Tangen (SINTEF)
Project Description
This project will kick-start the development of the Slicer-Liver extension that will be developed through the ALive project. The objective of the Slicer-Liver extension is to provide researchers with tools to perform liver analytics towards planning of liver interventions (resections, ablations). At this point in the project we need to port early prototypes of our resection planning algorithms into 3D Slicer.
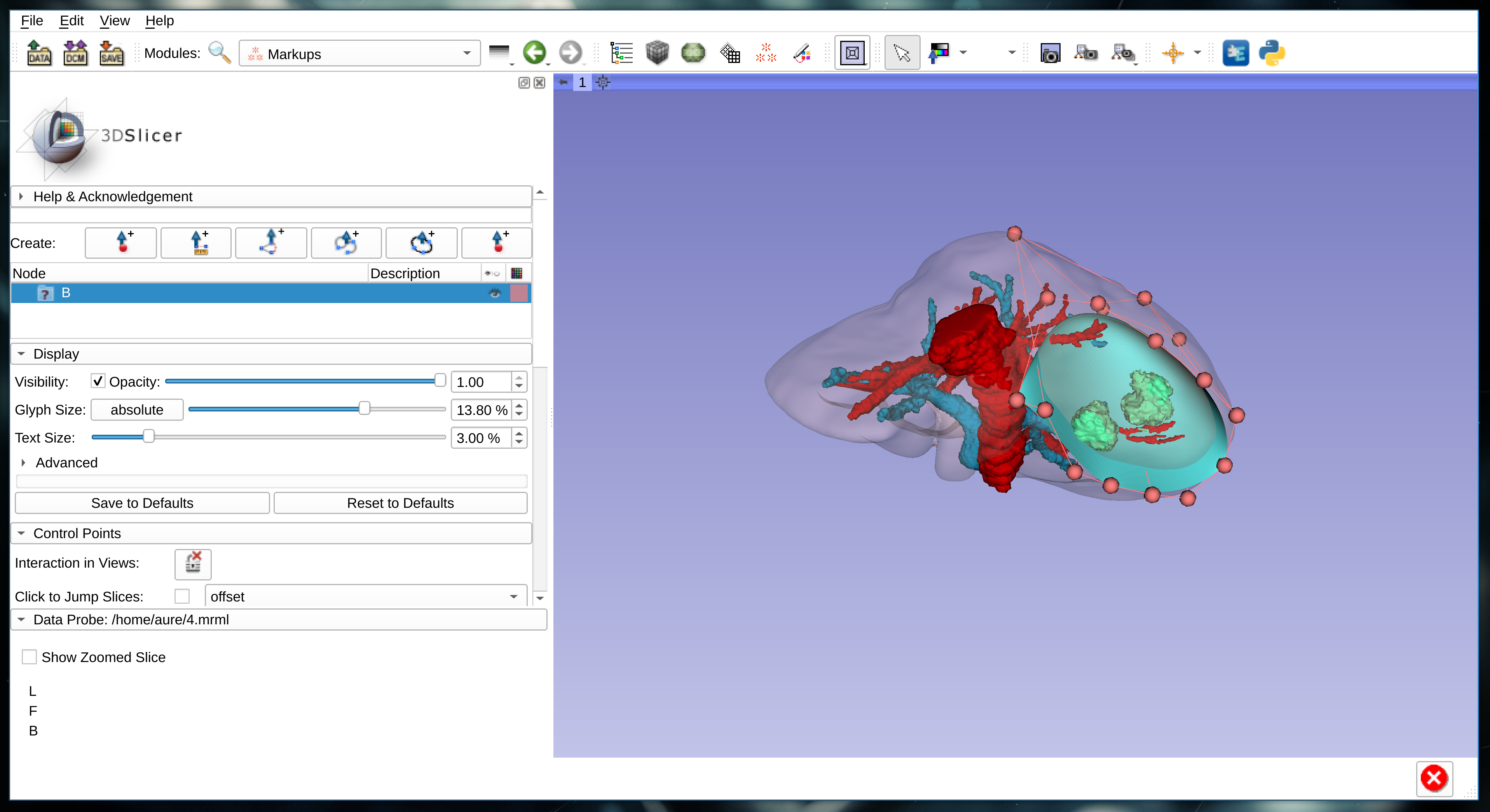
Early prototype of the resection planning module
Objective
- Integrate liver resection planning tools in a 3D Slicer extension.
Approach and Plan
- Development of a resection initialization widget using markups and shaders.
- Development of a deformables surface using markups.
- Development of interaction between the initialization markups and the deformable surface.
- Development of distance measurements visualized in the resections using shaders.
- Add a GUI to manage resections.
Progress and Next Steps
The core components of the planning platform have been developed but not integrated together. Shaders and pluggable markups infrastructure have been used for the development of the resection initialization, but are not yet integrated for visualization of other measurments (e.g., safety margins).
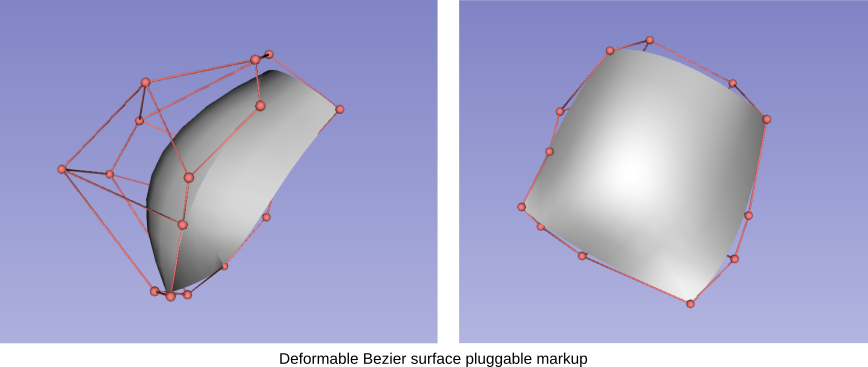
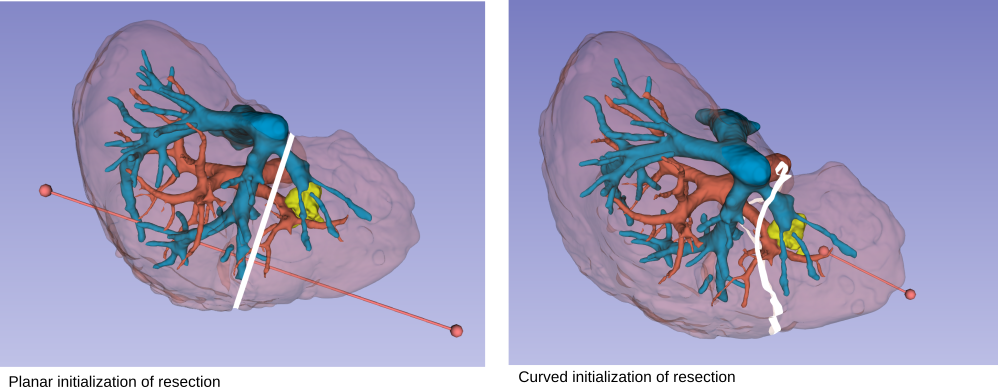
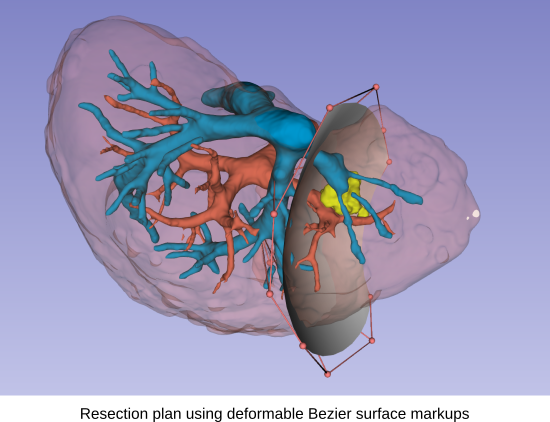
Our next steps are :
- Integrating all the resection components together
- Develop a Qt UI to drive the process
- Improve stability – software testing
- Improve performance – wider use of shaders
Background and References
- NorMIT-Plan at NA-MIC project week (December 2020)
- NorMIT-Plan at NA-MIC project week (january 2020)
- Palomar, Rafael, et al. “A novel method for planning liver resections using deformable Bézier surfaces and distance maps.” Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine 144 (2017): 135-45.
- Palomar, Rafael, et al. “Surface reconstruction for planning and navigation of liver resections.” Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics 53 (2016): 30-42.