 NA-MIC Project Weeks
NA-MIC Project Weeks
Back to Projects List
Real-time ultrasound AI segmentation using Tensorflow and PyTorch models
Key Investigators
- María Rosa Rodríguez Luque (Universidad de Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Spain) [on site]
- Tamas Ungi (Queen’s University, Canada) [remote]
- David García Mato (Ebatinca S.L., Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Spain) [on site]
- Chris Yeung (Queen’s University, Canada) [remote]
Project Description
The module “Segmentation U-Net”, from extension SlicerAIGT, applies deep learning models on an ultrasound image stream to generate the predicted segmentation in real time. This is shown in the following example, where it is used to detect tumour tissue (highlighted in red) on breast images. That way, we can apply a live volume reconstruction on this prediction and visualize the complete region of interest (in this case, the area of the tumour). Another instance, using spine images, is shown in (Figure 1).
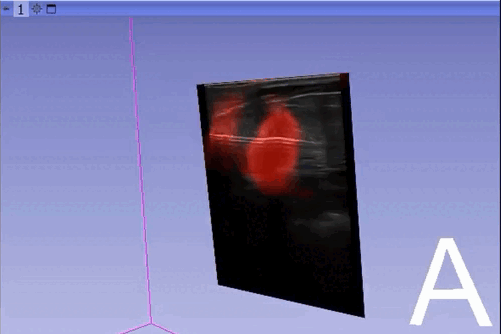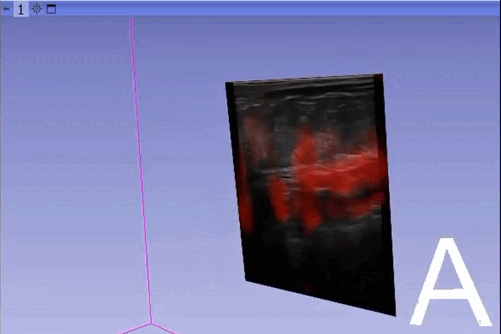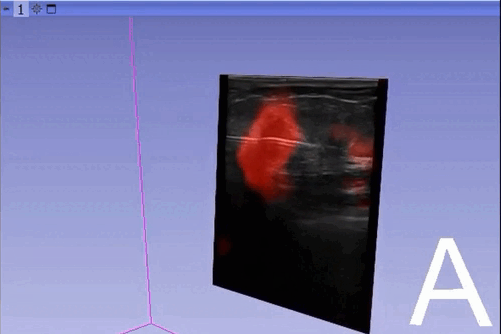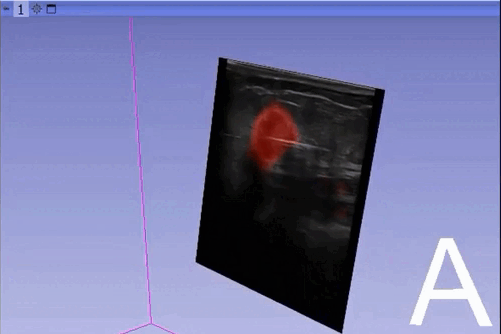

Currently, this module supports models trained with the TensorFlow ecosystem. However, in recent years, PyTorch has become an increasingly popular machine learning framework, especially in medical imaging applications (an example of this is the MONAI framework, which is based on PyTorch).
We have developed a separate module to run the inference of PyTorch model for the segmentation of breast ultrasound images: Breast Lesion Segmentation (Figure 2). However, our module does not integrate parallel processing to enable real-time image segmentation.
In this project, we aim to adapt the current “Segmentation U-Net” module to enable the use of models trained with both ecosystems, PyTorch and TensorFlow, for real-time ultrasound image segmentation.
In addition, we will discuss further improvements for this module. For instance, automatically visualize the prediction overlayed on the input ultrasound image and avoid changing to different modules to activate the visualization.
Objective
- Adapt the current “Segmentation U-Net” module to support models trained with PyTorch
- Automatically display the AI segmentation overlayed on the input ultrasound image
Approach and Plan
- Integrate a TensorFlow/PyTorch model selector, so the module would automatically use the one give by the user
- Develop the image pre-and post-processing required by the PyTorch model
- Record an ultrasound image stream and run the inference in real time using a PyTorch model
- Apply the selected prediction transform on the output volume automatically
Progress and Next Steps
- The module uses the file extension to know the model framework (.h5 for TensorFlow and .pth or .pt for PyTorch) and execute the corresponding actions in each case

- We have recorded a stream from a breast ultrasound phantom where an inclusion that simulates injured tissue is shown. A PyTorch model previously trained with the Dataset BUSI was used to run the inference for the real-time segmentation.
- Original stream recorded:

- Steps to run the inference and visualize the predicted segmentation with this new version of the “Segmentation U-Net” module:

- Lesion reconstruction using Volume Reconstruction and Volume Rendering modules:

- When we the box “Use separate process for prediction” is not checked, we automatically apply the prediction transform selected and display the AI segmentation overlayed on the input ultrasound image (as it was shown before). When this box is checked, the input stream and the prediction have different frame rate and it is more convenient to visualize the prediction in a different view, so we should make it visible manually.
Next Steps
-
Currently, it is required to define the PyTorch network and load only the trained weights. To make the module more flexible it is desired to directly load the complete model (as it is done in the case of TensorFlow).
-
The pre-and post-processings steps have been defined according to the process carried out to train the PyTorch model used in this case. However, these steps should be more generalized to work with different models.
-
PyTorch models are only supported when we use the same process for prediction (the check box is not selected), so it is necessary to improve this.
Illustrations
Previous work:
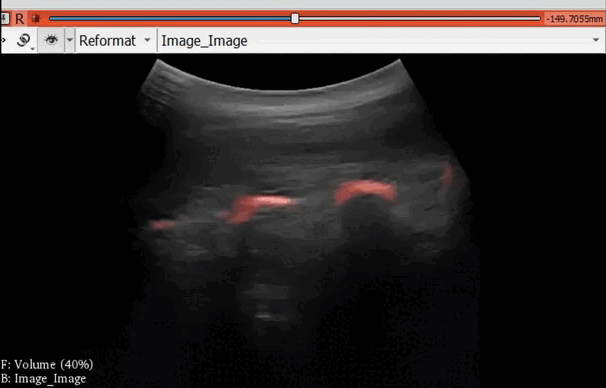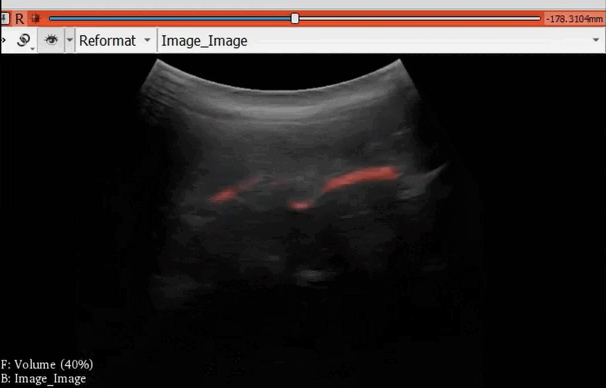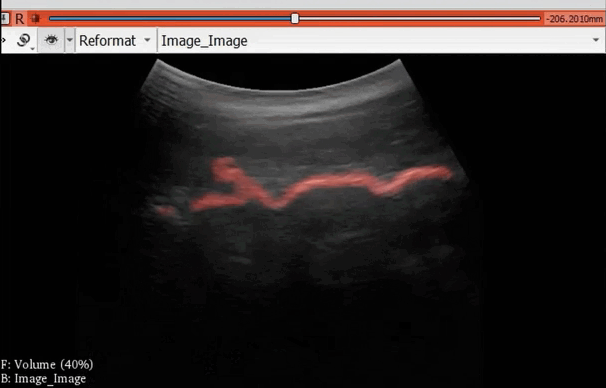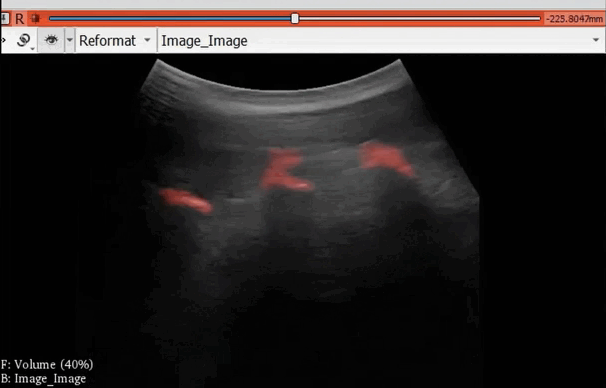

Figure 1. Real-time spine segmentation and volume reconstruction using the module “Segmentation U-Net”

Figure 2. Segmentation of breast ultrasound images using the module “Breast Lesion Segmentation”
Background and References
This project is based on the previous Segmentation Unet and Breast Lesion Segmentation modules:
- Segmentation Unet admits Tensorflow models to develop the segmentation task on an ultrasound image stream:
- GitHub repository: Segmentation Unet module.
- The tutorial about how to use the previous module was shown during PerkLabBootcamp held virtually on May 24-26, 2022.
- The video tutorials of the breast and spine segmentation are also available.
- Breast Lesion Segmentation deploy deep learning models trained in PyTorch for segmentation of 2D Ultrasound images:
- GitHub Repository: Breast Lesion Segmentation module.
Integration of PyTorch and Slicer:
- To use a deep learning model trained in PyTorch inside Slicer, we install the PyTorch extension, presented during 35th Project Week held virtually June 28-July 2, 2021.